- HISTORIC DNA EVIDENCE OF THE NATIVE AMERICAN PEOPLE
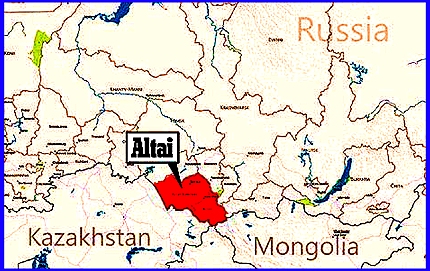
- “Scientists have long suspected that Native Americans are closely related to the peoples of Siberia and especially those of the Altai, which is a tiny region in Central Russia. The Altai people are believed to have migrated from Siberia across Chukotka and Alaska, and their descendants South to Tierra del Fuega in South America. The DNA evidence now Indicates that Native American ancestors initially reached America from Siberia at most 23,000 years ago, and later differentiating into today’s distinct groups.
- Now, after more than a century of speculation, an international group of geneticists using DNA evidence has proven that the Aztecs, Incas, Iroquois are closely related to the peoples of Altai, in the Siberian region that borders China and Mongolia. Altai is a key area because according to Dr. Theodore Schurr, from the University of Pennsylvania in the United States, people have been moving in and out of that area for thousands of years.
- WHERE IS THE ALTAI REGION? (MAP)
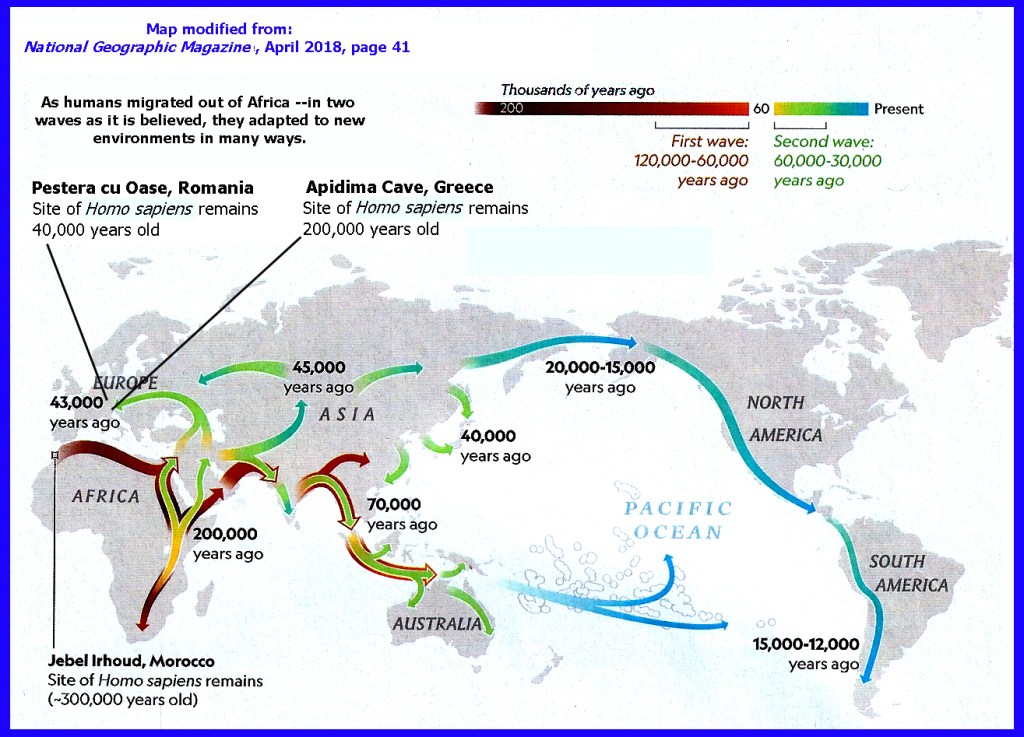
- HUMAN MIGRATION MAP, NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC, April 2018
- In 2015 the Russian geneticist, Oleg Balanovsky, finnaly confirmed the theory. In addition, Sr. Balanovsky’s studies also proved that some Native Americans have kinship with the Indigenous populations of Australia. Research by Valery Illyinsky at the RAS Institute of General Genetics confirms the theory that the Altal people are closely related to the Native American an tribes (see HE Yu 2020)
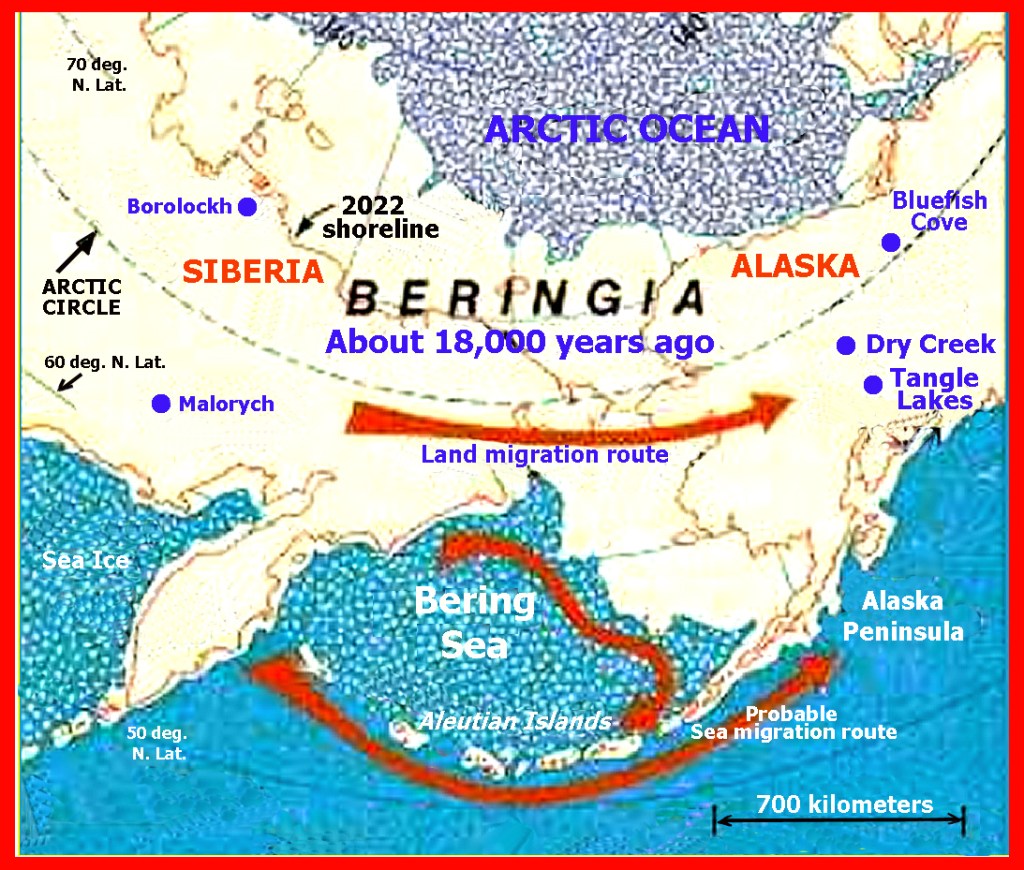
- Paleo Native Americans from Siberia would most likely have crossed into the Americas across Beringia when a Land Bridge was present. Paleo Siberians are closely related to Indigenous Americans, as well as to the East and SouthEast Asian groups, with whom they share a common origin from an ancestral East Asian source population in Mainland Southeast Asia. However, the occasional ancient contacts in America by people from other world geographic areas, such as japan, Middle East and Africa do not seem to have affected the genomes of the present day Native Americans significantly (See ethnic 1).
- Additional analyses of genetic markers has also been used to link groups of indigenous peoples. Studies focused on markers on the Y chromosome, which is always inherited by sons from their fathers. Haplogroup Q is a unique mutation shared among most indigenous peoples of the Americas. Studies have found that 93.8% of Siberia’s Ket people and 66.4% of Siberia’s Selkup people possess the mutation. The principal-component analysis suggests a close genetic relatedness between some northern Native Americans (the Chipewyan [Ojibwe] and the Cheyenne) and certain populations of central/southern Siberia (particularly the Kets, Yakuts, Selkups, and Altaians), at the resolution of major Y-chromosome haplogroups. This pattern agrees with the distribution of mtDNA haplogroup X, which is found in North America, is absent from eastern Siberia, but is present in the Altaians of southern central Siberia.
University of California, Riverside

